What Is Merchant Onboarding?
Merchant onboarding involves integrating new merchants or sellers onto a platform, such as an online marketplace, e-commerce site, or payment gateway. This process includes registering the merchants, verifying their information, and approving their accounts so they can begin selling their products or services on the platform. A streamlined onboarding process ensures compliance, mitigates risk, and enables merchants to start operations swiftly. This process not only sets the stage for the merchant’s transactions and interactions within a digital or physical commerce environment but also involves significant checks and balances to ensure security, compliance, and optimal functionality.
Essential Documentation For Merchant Onboarding
To streamline the merchant onboarding process and reduce potential delays, businesses in India should gather the necessary documents and materials beforehand. Being well-prepared can save time and ensure a smoother onboarding experience.
Here’s a list of essential documents and materials businesses should have ready for their merchant onboarding process in India:
1. Business Registration Documents
- Certificate of Incorporation
- Articles of Association (AOA) and Memorandum of Association (MOA)
- GST Registration Certificate
- Shops and Establishment Certificate (if applicable)
2. Tax Identification Numbers
- Permanent Account Number (PAN) of the business
- Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN)
3. Ownership Information
- Details about the business’s ownership structure, including information on owners, partners, or directors
- Personal identification documents for key stakeholders, such as an Aadhaar card, PAN card, passport, or driving licence
4. Financial Statements
- Recent financial documents, including balance sheets, profit and loss statements, and cash flow statements, provide insight into the business’s financial condition
5. Bank Account Information
- Details of the business’s bank account, including the account number, IFSC code, and the name and address of the bank
6. Business Licences and Permits
- Copies of relevant business licences, permits, or certifications required for operation in your industry or jurisdiction, such as FSSAI licence for food businesses or SEBI registration for financial services
7. Business Website and Online Presence
- Information about the business’s website, online store, or mobile app, including URLs and descriptions of products or services offered
8. Payment Processing History
- If available, statements or summaries of previous transaction volumes, chargeback rates, and other relevant payment processing history
9. Business Plan and Revenue Projections
- A comprehensive business plan, including revenue projections and anticipated transaction volumes, particularly important for startups or businesses with limited operational history
10. Compliance Documentation
Any documentation related to compliance with industry regulations or standards, such as:
- Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS)
- Data Privacy and Protection regulations
- Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) compliance
Having these documents ready can significantly facilitate the merchant onboarding process in India, allowing businesses to begin operations more quickly and efficiently.
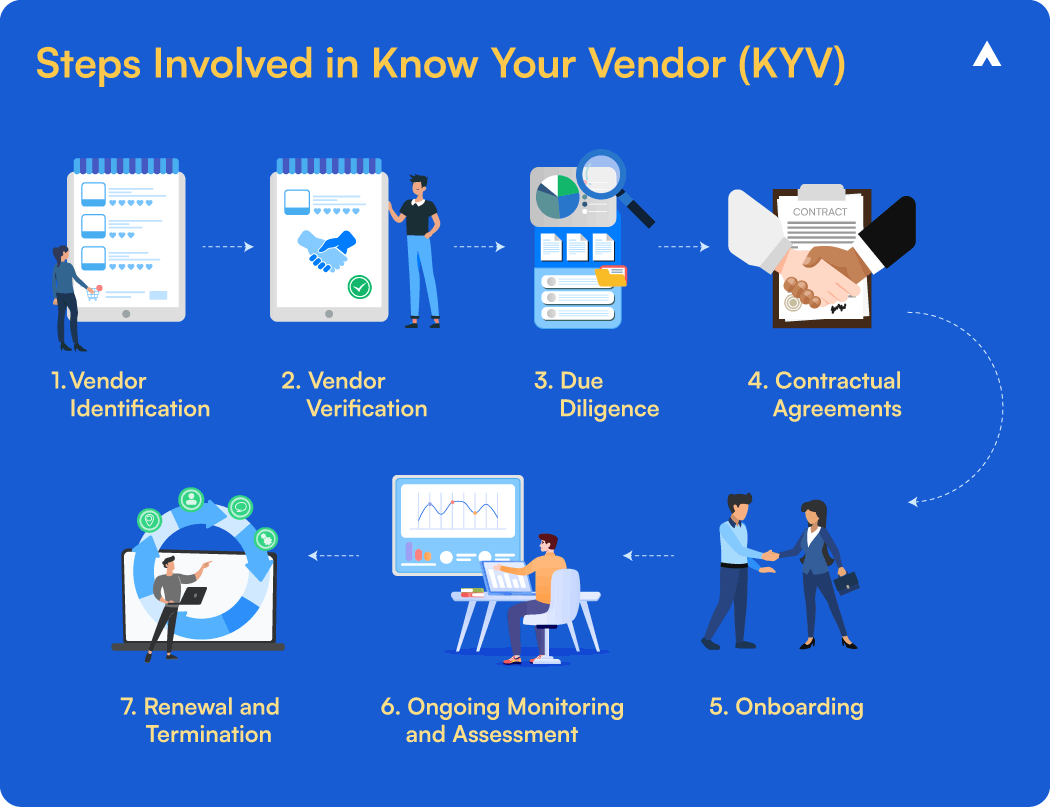
Step-by-Step Merchant Onboarding Process
The merchant onboarding process varies by industry and country, adhering to local regulations and law enforcement requirements. However, it generally follows these steps:
1. Processing Stage
2. KYB (Know Your Business) of Merchant
3. Merchant History Check
4. Verifying Ultimate Beneficial Owner (UBO)
5. Risk Assessment
6. Operational Analysis
What Are The Risks Involved In Merchant Onboarding?
The merchant onboarding process comes with various risks that Acquiring Banks, Payment Service Providers (PSPs), and Payment Aggregators (PAs) need to address effectively. Here’s an in-depth look at these risks:
1. Financial Risk
- Credit Risk: The possibility that a merchant might default on payments or fail to meet financial obligations. Evaluating a merchant’s creditworthiness and financial health is crucial.
- Chargebacks: Frequent chargebacks can indicate fraudulent activity, poor service, or dissatisfaction among customers, impacting the financial stability of the business.
2. Operational Risk
- Business Continuity: Assessing the merchant’s ability to continue operations without interruption is essential. Disruptions can affect the supply chain and overall business operations.
- Process Reliability: Ensuring that the merchant’s operational processes are dependable and consistently meet service standards. This includes timely delivery of goods and services.
3. Reputational Risk
- Brand Association: The risk that a merchant’s negative reputation or actions will impact the business’s brand image. Poor performance or unethical practices by a merchant can harm the primary business’s reputation.
- Customer Satisfaction: If a merchant provides poor service, it can lead to dissatisfied customers, negative reviews, and potential loss of business.
4. Regulatory and Compliance Risk
- Legal Compliance: Ensuring that merchants adhere to all relevant laws and regulations to avoid legal penalties. This includes compliance with industry-specific regulations.
- Data Security: Verifying that merchants follow data protection regulations to safeguard customer information. This is critical in preventing data breaches and maintaining customer trust.
5. Fraud Risk
- Transaction Fraud: The risk that a merchant might engage in fraudulent transactions, leading to financial losses for the partnering company.
- Identity Theft: Ensuring that the merchant’s identity and business credentials are legitimate to prevent identity fraud.
6. Supply Chain Risk
- Supplier Reliability: The risk that a merchant might fail to deliver goods or services as agreed, disrupting the supply chain.
- Quality Control: Ensuring that the products or services provided by the merchant meet the required quality standards.
7. Technological Risk
- System Integration: Ensuring that the merchant’s technology and systems integrate seamlessly with your own to avoid operational disruptions.
- Cybersecurity: Assessing the merchant’s cybersecurity measures to protect against data breaches and cyberattacks.
8. Contractual Risk
- Contract Clarity: Ensuring that contracts with merchants are clear, comprehensive, and enforceable.
- Dispute Resolution: Having clear mechanisms in place for resolving disputes that may arise with merchants.
Mitigating Merchant Risk
1. Due Diligence and Vetting:
Thorough background checks on merchants, including financial health, legal compliance, and reputational standing, are essential for mitigating risks. Third-party verification services can validate merchant credentials and performance history.
2. Continuous Monitoring:
Ongoing monitoring of merchant activities helps detect and address issues promptly. Real-time data analytics can identify potential risks and enable corrective action before problems escalate.
3. Contractual Agreements:
Comprehensive contracts outlining expectations, responsibilities, and liabilities of both parties help manage risks. Regular audits, compliance checks, and penalties for non-compliance should be included in these agreements.
4. Technology Solutions:
Advanced risk management software and tools can automate risk assessment and monitoring processes. AI and machine learning can predict potential risks and proactively mitigate them, enhancing overall risk management.
5. Training and Awareness
Regular training for employees on risk management practices and raising awareness about potential merchant risks can prevent issues. Knowledgeable staff can recognize and address risks before they escalate.
6. Diversification of Suppliers
Diversifying the supplier base reduces over-reliance on a single merchant, mitigating the impact of any single merchant’s failure on business operations.
7. Regular Audits and Assessments
Periodic audits and assessments ensure ongoing compliance and performance. Identifying and rectifying potential issues early helps maintain high standards.
8. Insurance and Risk Transfer
Insurance options covering merchant-related risks can mitigate financial impacts. Transferring some risks to an insurance provider offers additional protection.
Merchant Monitoring
Ongoing Risk Management
Merchant acquirers of payment service providers (PSPs) must continue risk management efforts even after onboarding a new merchant. If a merchant changes the nature of their business or if there is a sudden change in transaction volume or amounts, the merchant must be re-evaluated for risk. Quick re-evaluation is essential to mitigate potential damage.
Key Merchant Monitoring Practices
Merchant monitoring practices should include checks for:
- Exceeding transaction thresholds
- Spikes in transaction activities
- Changes on the merchant’s website, such as product updates or new links
- Inclusion of individuals on sanction lists
- Unusual cross-border transactions
- Negative media mentions
While automation in monitoring has been largely successful, it comes with challenges, such as false positives. Despite this, automation is generally considered better than manual monitoring. Issues can arise when merchants start selling in new markets or offering new products, as the technology may not always keep pace. This makes the industry increasingly competitive and challenging.
Merchant Onboarding With AuthBridge
Merchant onboarding is a critical process that involves verifying the legitimacy and risk levels of businesses before they are allowed to process payments. AuthBridge offers comprehensive solutions to streamline and secure this process, ensuring businesses meet all necessary compliance standards. Here’s how AuthBridge enhances the merchant onboarding experience:
- Streamlined Document Collection and Verification
AuthBridge facilitates the efficient collection and verification of essential documents, such as business registration papers, tax identification numbers, and ownership information. Their automated systems ensure accuracy and reduce the time required for initial verification.
- Comprehensive KYC and KYB Compliance
AuthBridge employs advanced Know Your Customer (KYC) and Know Your Business (KYB) protocols to verify the identity and legitimacy of merchants. This includes background checks and ongoing monitoring to prevent fraud and financial crimes.
- Enhanced Security Measures
By integrating robust security measures, AuthBridge helps protect against financial crimes like money laundering and terrorist financing. Their systems continuously monitor for suspicious activities and ensure compliance with industry standards such as AML (Anti-Money Laundering) regulations.
- Detailed Merchant History Checks
AuthBridge conducts in-depth checks on the merchant’s financial history, including past transactions and dealings. This helps identify any previous issues with fraud or chargebacks, ensuring that only trustworthy merchants are onboarded.
- Efficient Risk Assessment
AuthBridge’s risk assessment tools categorize merchants based on their risk levels, ranging from very low to very high. This allows payment service providers to make informed decisions and implement appropriate measures before merchant onboarding.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Re-evaluation
Even after onboarding, AuthBridge continues to monitor merchants for any changes in their business activities or risk profiles. This includes tracking transaction volumes, website updates, and compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring that any potential risks are identified and addressed promptly.
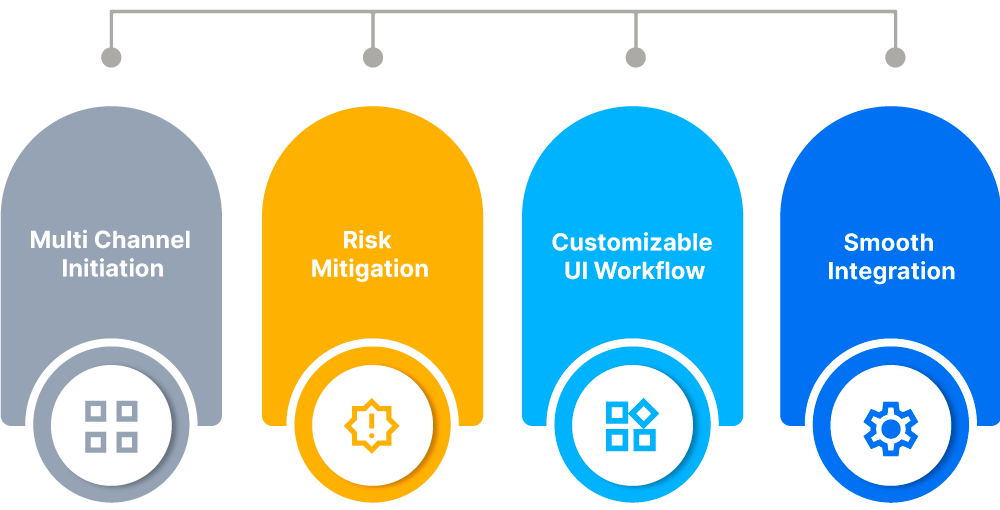
- Seamless Integration and User Experience
AuthBridge’s solutions are designed to integrate seamlessly with existing systems, providing a smooth and user-friendly onboarding experience. Their automated processes reduce manual intervention, minimize errors, and speed up the overall onboarding timeline.