What is Vendor Compliance ?
Vendor compliance is fundamental in orchestrating a streamlined supply chain, safeguarding quality, and mitigating risks across various fronts. In today’s global economy, where supply chains are extensive and regulatory environments are complex, the role of vendor compliance has become more crucial than ever.
A well-managed vendor compliance program is essential for reducing disruptions and ensuring smoother operations within supply chains. Compliance standards help standardise procedures, leading to fewer errors and delays.
Importance of Vendor Compliance
Research from the Supply Chain Management Review indicates that companies with robust compliance programs see a 60% reduction in supply chain inefficiencies, leading to a more predictable delivery schedule and reduced cost of operations.
By emphasizing the Indian market’s specificity, this guide aims to arm businesses with the knowledge to navigate the complexities of vendor management successfully.
Major retailers like Walmart have implemented stringent compliance requirements for their suppliers to ensure timely deliveries and reduce stocking issues, which has resulted in a marked improvement in their inventory turnover ratios.
Risks associated with Non-Compliance of Vendor Onboarding
Failure to comply with regulatory and internal standards during the vendor onboarding process can expose a company to a variety of risks. Here’s an in-depth look at the potential dangers of non-compliance in vendor onboarding.
Financial Risks
Increased Costs and Penalties:
- Fines and Penalties: Non-compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Anti-Money Laundering (AML) laws, or the Sarbanes-Oxley Act can result in substantial fines.
- Overpayment: Without proper due diligence, a company might end up contracting vendors at prices above market rates or for subpar services, impacting financial health.
Fraud and Misappropriation:
- Vendors not properly vetted can engage in fraudulent activities, leading to direct financial losses and potentially long-term financial liabilities.
Operational Risks
Supply Chain Disruptions:
- Inadequately vetted vendors may fail to meet contractual obligations regarding quality, timeliness, or specifications, leading to disruptions in production and service delivery.
Quality Control Failures:
- Non-compliance can result in working with vendors who do not adhere to industry standards or regulatory requirements, impacting the quality of the end products or services.
Legal Risks
Breach of Contract:
- Vendors who have not been properly onboarded may not fully understand their contractual obligations, leading to breaches that could have legal repercussions.
Liability Issues:
- If a vendor fails to comply with legal standards, especially in industries like pharmaceuticals, food service, or construction, the client company may face lawsuits or legal scrutiny.
Reputational Risks
Brand Damage:
- Association with non-compliant vendors can damage a company’s reputation, affecting customer trust and leading to decreased sales.
Loss of Investor Confidence:
- Investors are increasingly attentive to compliance and ethical operations; non-compliance can lead to loss of investor confidence and potential divestment.
Security Risks
Data Breaches:
- Vendors without robust cybersecurity measures can become the weak links through which cyberattacks can occur, leading to significant data breaches.
Intellectual Property Theft:
- If intellectual property is not adequately protected in vendor agreements, there is a risk of IP theft, which can jeopardize business competitiveness.
Compliance Risks
Regulatory Sanctions:
- Failure to adhere to industry regulations can lead to sanctions, including the inability to operate in certain jurisdictions or sectors.
Increased Scrutiny and Audits:
- Non-compliance can trigger more frequent and rigorous audits by regulatory bodies, increasing operational overhead and distracting from core business activities.
Best Practices for Mitigating Risks in Vendor Onboarding
A recent study highlighted that 55% of consumers are willing to pay more for products from companies with strong compliance records, indicating the reputational value of compliance.
Implement Comprehensive Screening Processes:
Conduct thorough due diligence that includes financial, legal, and compliance checks before formalizing any vendor relationships.
Standardize Onboarding Procedures:
Develop a standardized onboarding framework that includes checks and balances at each stage of the process.
Leverage Technology:
Utilize technology solutions for vendor management that can automate parts of the onboarding process and ensure consistent application of standards.
Regularly Update Compliance Requirements:
Keep up-to-date with changes in regulatory standards and update vendor onboarding processes accordingly.
Foster Strong Vendor Relationships:
Engage regularly with vendors to reinforce compliance requirements and foster a mutual understanding of operational expectations.
Key Areas of Vendor Compliance
Vendor compliance is a critical component of modern business operations, spanning various domains that ensure legal, ethical, and operational integrity. This section explores each key area of vendor compliance in detail, integrating statistical data and industry standards to underscore their importance.
Contractual Obligations
The adherence to contractual obligations is fundamental to maintaining trust and consistency in business relationships. Contracts govern nearly every facet of these relationships, from the scope of work to quality specifications and timelines. Utilising advanced contract management systems can lead to a 40% improvement in compliance levels, according to the Association for Contract Management. These systems enable businesses to automate and monitor contract performance, ensuring that all parties meet their agreed-upon obligations efficiently. Utilising standards such as ISO 9001 can help organisations streamline contract management processes by aligning them with globally recognised best practices.
Regulatory Compliance
Navigating the complex landscape of regulatory compliance is crucial for businesses to avoid legal penalties and operational disruptions. Vendors must comply with local, national, and international regulations, which vary significantly across industries. A study by a leading consultancy firm highlighted that companies with integrated compliance management systems reduce their risk of regulatory penalties by up to 70%. Regular training sessions and compliance audits are essential components of a robust regulatory compliance strategy. In the pharmaceutical industry, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) is crucial for maintaining compliance with FDA regulations.
Quality Standards
Quality compliance ensures that products and services meet predefined standards and customer expectations, which is critical for maintaining brand reputation and customer loyalty. Industries report that consistent application of quality standards like Six Sigma and Lean methodologies can reduce defect rates by up to 50%. Regular audits and quality checks are essential to maintain these standards. According to ISO, organisations adhering to ISO 9001 quality management standards have seen a 75% increase in customer satisfaction scores.
Data Security
As digital transactions become more prevalent, ensuring data security compliance is paramount to protect sensitive information against breaches and cyber-attacks. Implementing standards such as ISO/IEC 27001 for information security management helps organisations manage the security of assets such as financial information, intellectual property, employee details, and information entrusted by third parties. The Global Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) enforcement report states that compliance with data security standards can decrease the likelihood of data breaches by up to 80%.
Sustainability Practices
Sustainability compliance is increasingly important as businesses and consumers alike are becoming more environmentally conscious. Vendors are expected to adhere to practices that reduce environmental impact. A report by the United Nations Global Compact indicates that companies enforcing sustainability standards across their supply chains see an average reduction in carbon emissions of 22%. Following the ISO 14001 Environmental Management System standards helps vendors minimise their environmental footprint through more efficient resource use and waste management.
Social Responsibility
Maintaining ethical labour practices and responsible sourcing are essential for social compliance. This safeguards against labour rights abuses and promotes fair trade practices. Adherence to the SA8000 standard, an auditable certification standard that encourages organizations to develop, maintain, and apply socially acceptable practices in the workplace, is seen as a benchmark in ethical compliance. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), businesses that implement strict social compliance programs see a 30% decrease in worker grievances and a significant improvement in workplace relations.
Establishing a Vendor Compliance Program
Developing a successful vendor compliance program is a strategic endeavor that involves detailed planning and execution. Such a program ensures that vendors align with your organization’s ethical, legal, and operational standards, creating a compliance-centric culture and partnership.
Developing Clear Vendor Selection Criteria
The cornerstone of a strong vendor compliance program is setting rigorous selection criteria that evaluate potential vendors not only on their ability to deliver the required goods and services but also on their compliance with industry standards and ethical practices. For example, companies like Apple Inc. enforce a Supplier Code of Conduct that mandates compliance with environmental practices and labour laws before onboarding vendors.
International standards such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management) can be integral to these criteria, ensuring that vendors meet global quality standards, which are crucial for maintaining product integrity and customer satisfaction.
Negotiating Vendor Contracts
Effective contracts are essential for outlining compliance expectations clearly. These contracts should detail every compliance requirement, from regulatory adherence to ethical standards and quality commitments. For instance, multinational corporations often include clauses that require vendors to adhere to the United Nations Global Compact principles, which cover human rights, labour, environment, and anti-corruption policies.
Including stipulations for regular compliance audits and setting out clear penalties for non-compliance ensures that vendors are held accountable. Contracts should also include provisions for remediation strategies and, if necessary, termination protocols to manage non-compliance effectively.
Implementing Onboarding Procedures
A thorough onboarding process is crucial for aligning vendor operations with your compliance standards. This involves comprehensive training sessions tailored to various aspects of your compliance requirements, supplemented by detailed manuals or digital resources. For example, a company like Siemens uses digital platforms to provide interactive training modules that cover everything from safety standards to anti-corruption laws.
Establishing robust communication channels during onboarding helps in addressing compliance questions quickly, ensuring vendors understand their obligations from the start.
Monitoring Vendor Performance
Ongoing monitoring is vital to ensure continuous compliance. Regular audits, whether internal or by third-party auditors, play a critical role in this process. Industries regulated under FDA or EMA guidelines, for example, require stringent compliance monitoring, including surprise audits and regular performance reviews.
Implementing technology solutions like compliance dashboards can provide real-time monitoring of vendor activities, allowing quick responses to potential compliance breaches.
Enforcing Compliance Policies
Enforcement of compliance policies must be consistent and transparent. This includes applying penalties for non-compliance as well as recognizing and rewarding compliance excellence. For instance, companies might implement a tiered vendor rating system where vendors meeting certain compliance criteria receive benefits such as longer contract terms or more favourable payment terms.
Regularly updating enforcement policies to reflect new regulatory requirements and market conditions is also crucial for maintaining an effective compliance program.
Benefits of Vendor Compliance
Ensuring that vendors comply with these directives is crucial for maintaining efficient operations and achieving strategic business goals. Below are the key benefits of effective vendor compliance:
Improved Supply Chain Efficiency
Streamlined Operations:
- Compliance ensures that vendors follow standardized procedures, leading to smoother operations and less administrative burden.
- Streamlined processes minimize delays caused by errors or inconsistencies, optimizing the supply chain flow.
Predictable Delivery and Quality:
- Vendors who adhere to compliance standards consistently deliver products and services on time and meet quality specifications, reducing the need for rework and adjustments.
Enhanced Risk Management
Reduced Operational Risks:
- Compliance reduces the risk of supply chain disruptions caused by vendor errors or failures.
- It minimizes exposure to risks related to safety, quality, and environmental standards.
Legal and Regulatory Adherence:
- Ensures that vendors operate in accordance with relevant laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal penalties and fines for both the vendor and the company.
Cost Management and Savings
Cost Efficiency:
- Compliance helps avoid costs related to non-conformance such as penalties, returns, and rejections.
- Streamlined processes reduce overhead costs by minimizing the need for checks and audits.
Negotiation Leverage:
- Compliance track records can provide leverage in negotiating better terms with vendors, including pricing, payment terms, and delivery schedules.
Enhanced Brand Reputation and Trust
Brand Protection:
- Compliance with environmental, safety, and labor standards protects the company’s brand reputation from the negative impact of vendor practices.
- It ensures ethical supply chain practices, which can boost brand image and customer loyalty.
Consumer Confidence:
- Customers are increasingly concerned with how products are sourced and created. Compliance ensures transparency and ethical practices, enhancing consumer trust.
Better Relationship Management
Stronger Vendor Relationships:
- Clear compliance guidelines provide a framework for open communication and mutual expectations, fostering stronger relationships.
- Compliance-related discussions can lead to better understanding and cooperation between the company and its vendors.
Vendor Development:
- Compliance programs often include training and development, which can improve vendor capabilities and performance over time.
Technological Integration and Innovation
Technology Adoption:
- Implementing compliance often requires advanced technological solutions, which can lead to greater innovation and efficiency in operations.
- Technology used in compliance tracking, like RFID and blockchain, can improve data accuracy and visibility.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Better Analytics and Reporting:
- Compliance programs generate data that can be analyzed to improve procurement strategies and supply chain management.
- Enhanced visibility into vendor performance helps in making informed, strategic decisions.
Continuous Improvement of the Compliance Program
Vendor compliance programs should evolve based on ongoing reviews and feedback. Engaging with vendors to gain insights into the effectiveness of your program can reveal opportunities for improvement. For example, annual vendor conferences can be a platform for discussing compliance challenges and brainstorming improvements, fostering a collaborative environment for compliance enhancement.
This approach not only improves the program’s effectiveness but also strengthens vendor relationships by building a foundation of mutual respect and cooperation.
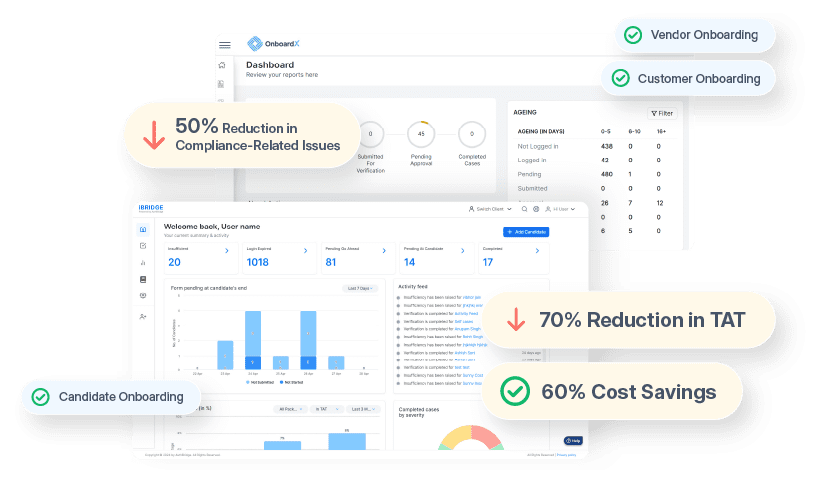
OnboardX By AuthBridge
Welcome to the Future of Vendor Management, OnboardX: The Comprehensive Platform for end-to-end Third-Party Onboarding and Verification. Say goodbye to the hurdles of inefficiency, data disparities, and regulatory complexities.
Adopt a path of automated processes, scalable operations, and cutting-edge analytics to elevate your vendor relationship management to new heights.
As leaders in the world of BGV and due-diligence, our one stop onboarding solution aims to provide seamless onboarding to organisations by offering features such as:
- Case approval workflow with payment and contract signing
- Custom communication options in emails and WhatsApp
- 160+ real-time checks and verifications
- Personalized and customizable solution
- Seamless API integration
- Fully automated journey with multiple touch points and clear visibility
Why Choose OnboardX?
OnboardX is a comprehensive one-stop solution for all your vendor onboarding needs and here a few reasons why we think it will be the best suited solution for your needs:
- Unmatched Flexibility: A low-code platform allowing fast, custom solution development with minimal technical skill requirements.
- Comprehensive Integration: Deep integration capabilities with major ERP and P2P suites, serving as a central third-party data layer.
- Advanced Third-Party Data Management: Expertise in managing complex and continuously changing third-party data, with more than 18+ years of enterprise experience.
- Targeted Solutions Over Generic Tools: Specific focus on third-party data, differentiating from generic P2P suites, MDM solutions, and in-house systems.
Pre-Integrated APIs: Comes with pre-integrated APIs and proprietary databases for faster turn-around time and comprehensive verification processes. - Easy on Pockets: Consolidate data collection, verification, and signature processes into a single, budget-friendly solution. Say goodbye to fragmented expenses on multiple tools – OnboardX streamlines it all for the price of one.
- Dedicated Third Party Expertise: Dedicated team focused on vendor management solutions, ensuring specialised knowledge and tailored services.