What is Due Diligence?
According to Investopedia, the term due diligence refers to an investigation, audit, or review performed to confirm facts or details of a matter under consideration.
In the context of a business, due diligence means employing KYC/KYB procedures to ensure compliance, prevent fraud, and minimize risk exposure associated with various business processes. Its need arises in case of business transactions like acquisitions, customer & third-party onboarding, related party compliance, and even in the hiring process of employees.
The process can include reviewing financial statements, database checks, interviewing management, site visits, process audits, and assessing the company’s market position and competitive landscape.
To ensure a risk-free business ecosystem, you need to understand the key aspects of due diligence that your business needs to focus upon. Don’t worry we have got you covered.
Here is what you can expect to learn from this article:
- What is due diligence?
- Importance of Due Diligence in Today’s World
- Types of Due Diligence
- Rules, Regulations, and Penalties around Due Diligence
- What are your due diligence needs?
- Risk Score-Based Due Diligence Process
- Levels of Due Diligence
- Implementing Measures of Due Diligence
- Due Diligence Solutions and Reports
Importance of Due Diligence in Today’s World
The need for due diligence becomes all the more imminent with ever-evolving technology, and external factors like the pandemic. Trustable business partners and transparent business processes are key to resilience for business owners today. The abundance of digital footprints of customers, business partners and third parties has opened a world of possibilities for fraudulent activities and their associated risk exposure. Traditional due diligence methods are becoming redundant given the complexity of information and lack of appropriate due diligence frameworks.
Businesses are adopting new-age due diligence solutions to minimise their risk exposure, ensure compliance and prevent fraud. As a result, the global fraud detection and prevention industry is seeing a steep spike in demand with more and more innovative solutions coming in every day.
Types of Due Diligence Audits
Following are some of the types of audits for due diligence:
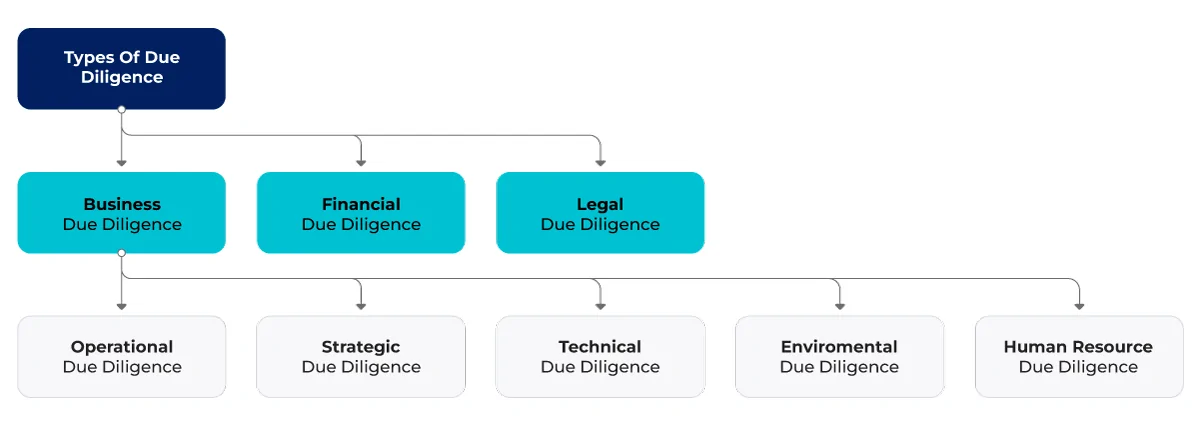
Supply Chain Due Diligence Audit: This audit examines a company’s potential suppliers to identify risks associated with their operations. It considers legislative, governance, ethical, and environmental risks:
- Legislative Risks: Ensure that suppliers comply with relevant laws and regulations, including labor laws, environmental regulations, and industry-specific standards.
- Governance Risks: Assess the management structure of suppliers, including internal controls, transparency, and accountability measures.
- Ethical Risks: Examine suppliers’ business practices, including their stance on corruption, fair wages, and working conditions.
- Environmental Risks: Evaluate suppliers’ environmental practices, including their carbon footprint, waste management, and sustainability initiatives.
Tax Due Diligence Audit: This audit identifies and analyzes potential tax exposures on the buy side of a transaction, aiming to protect the buyer from unforeseen tax liabilities:
- Tax Risk Assessment: Examine the target company’s tax filings, compliance history, and potential liabilities.
- Tax Mitigation Mechanisms: Ensure protections for the buyer, including tax warranties and indemnities, reducing financial risk.
Market Due Diligence Audit: Unlike other audits that rely on internal information, this audit gathers information from external sources to evaluate the market environment:
- Industry Experts: Consult with industry experts to understand market trends, challenges, and opportunities.
- Competitors: Analyze competitors’ positioning, pricing strategies, and market share to evaluate the target company’s competitive edge.
- Customers: Gather feedback from customers to assess brand perception, loyalty, and demand trends.
Management Due Diligence Audit: This audit evaluates a company’s senior management, assessing their effectiveness in achieving strategic objectives:
- Management Structure: Review the hierarchy, roles, and responsibilities of key executives.
- Leadership Effectiveness: Evaluate the decision-making abilities, vision, and strategic alignment of senior management.
- Track Record: Analyze past performance to assess management’s ability to navigate challenges and drive growth.
Information Systems Due Diligence Audit: This audit reviews a company’s IT infrastructure, uncovering performance, liabilities, risks, and opportunities:
- IT Performance: Assess the efficiency, scalability, and stability of IT systems supporting the business.
- Security and Liabilities: Evaluate cybersecurity measures, data protection policies, and potential vulnerabilities.
- Investment Needs: Identify opportunities for IT enhancements, upgrades, and investment to support business growth.
Reconciliation Due Diligence Audit: This audit compares transactions and activities with supporting documentation, resolving discrepancies:
- Internal Reconciliation: Compare internal financial records, identifying inconsistencies and ensuring accuracy.
- External Reconciliation: Engage an external auditor to conduct a yearly reconciliation, confirming the accuracy of financial statements.
- Bank Reconciliation: Compare bank statements to internal records, identifying financial gaps or discrepancies.
Legal Due Diligence Audit: This audit evaluates the legal matters of a company, deal, or transaction:
- Contractual Obligations: Review contracts, agreements, and deals to ensure legal compliance and protect the company.
- Legal Risks: Assess ongoing litigation, potential disputes, and regulatory compliance to identify potential risks.
- Legal Protections: Ensure adequate legal safeguards to protect the company’s interests.
Environmental Due Diligence Audit: This audit evaluates a property’s environmental conditions and risks:
- Environmental Risks: Assess potential hazards, including pollution, contamination, and waste management.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations, reducing legal liabilities.
- Sustainability: Evaluate sustainability initiatives and practices, including renewable energy use, to assess environmental impact.
Operational Due Diligence Audit: This audit reviews the operational aspects of a target company during mergers and acquisitions:
- Process Efficiency: Evaluate the efficiency of supply chain management, production processes, and overall operational effectiveness.
- Cost Management: Assess cost structures, identifying opportunities for optimization and cost-saving measures.
- Operational Sustainability: Ensure that the company’s operations can support future growth and maintain profitability.
Step-by-Step Due Diligence Process:
To give readers a clearer understanding of how due diligence audits work, here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
Preparation: Identify the scope and objectives of the audit, determining which areas to examine and the key questions to address. This step involves gathering a list of necessary documents and data sources.
Document Collection and Review: Gather and review relevant documents such as financial statements, contracts, and operational reports. This stage provides the foundational data for analysis.
Analysis: Conduct an in-depth analysis of the collected data, assessing financial performance, operational efficiency, legal risks, and market positioning. This step may involve collaboration with subject matter experts.
Report Generation: Compile the findings into a comprehensive report, highlighting key insights, risks, and recommendations. The report should be clear and actionable, guiding decision-making.
Follow-Up: Present the report to relevant stakeholders and follow up on recommended actions. This stage ensures that the insights from the audit are utilized effectively.
Comprehensive Due Diligence Audit Checklist
This concise checklist provides a streamlined overview of key areas in due diligence audits, guiding businesses through financial, legal, operational, and other critical stages for informed decision-making and risk mitigation.
Scope Definition:
- Define the audit’s scope and objectives, outlining key areas to be examined and required data sources.
Financial Due Diligence:
- Statements: Review financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement) for accuracy and consistency.
- Liabilities: Examine debts, obligations, and financial risks.
- Forecast: Assess budgets and financial projections to gauge growth potential.
Legal Due Diligence:
- Contracts: Review key contracts, ensuring compliance and identifying liabilities.
- Litigation: Identify ongoing or potential legal disputes, assessing impact.
- Regulatory: Ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations.
Operational Due Diligence:
- Supply Chain: Evaluate supply chain efficiency and stability, identifying potential disruptions.
- Production: Assess production capacity, efficiency, and scalability.
- Costs: Review cost structures, identifying opportunities for optimization.
Market Due Diligence:
- Competitors: Analyze competitors’ positioning, pricing strategies, and market share.
- Customers: Gather customer feedback to assess brand perception, loyalty, and demand.
- Trends: Evaluate industry trends, identifying opportunities and threats.
Management Due Diligence:
- Leadership: Evaluate senior management’s effectiveness, vision, and alignment.
- Track Record: Assess past performance and management’s ability to navigate challenges.
- Succession: Ensure a succession plan is in place to minimize disruptions.
IT Due Diligence:
- Infrastructure: Review IT systems’ performance, scalability, and stability.
- Security: Evaluate cybersecurity measures, data protection policies, and vulnerabilities.
- Upgrades: Identify opportunities for IT enhancements to support growth.
Environmental Due Diligence:
- Risks: Assess potential hazards like pollution, contamination, and waste management.
- Sustainability: Evaluate sustainability initiatives and practices.
- Compliance: Ensure compliance with environmental laws and regulations.
Reconciliation Due Diligence:
- Internal: Compare internal financial records, identifying inconsistencies.
- Bank: Compare bank statements to internal records, identifying gaps or discrepancies.
- External: Engage an external auditor for annual reconciliation to ensure accuracy.
Report Generation:
- Findings: Compile findings into a comprehensive report, highlighting key insights, risks, and recommendations.
- Presentation: Present the report to stakeholders, ensuring actionable steps.
- Follow-Up: Monitor progress on recommendations, ensuring implementation.
Rules, Regulations and Penalties around Due Diligence
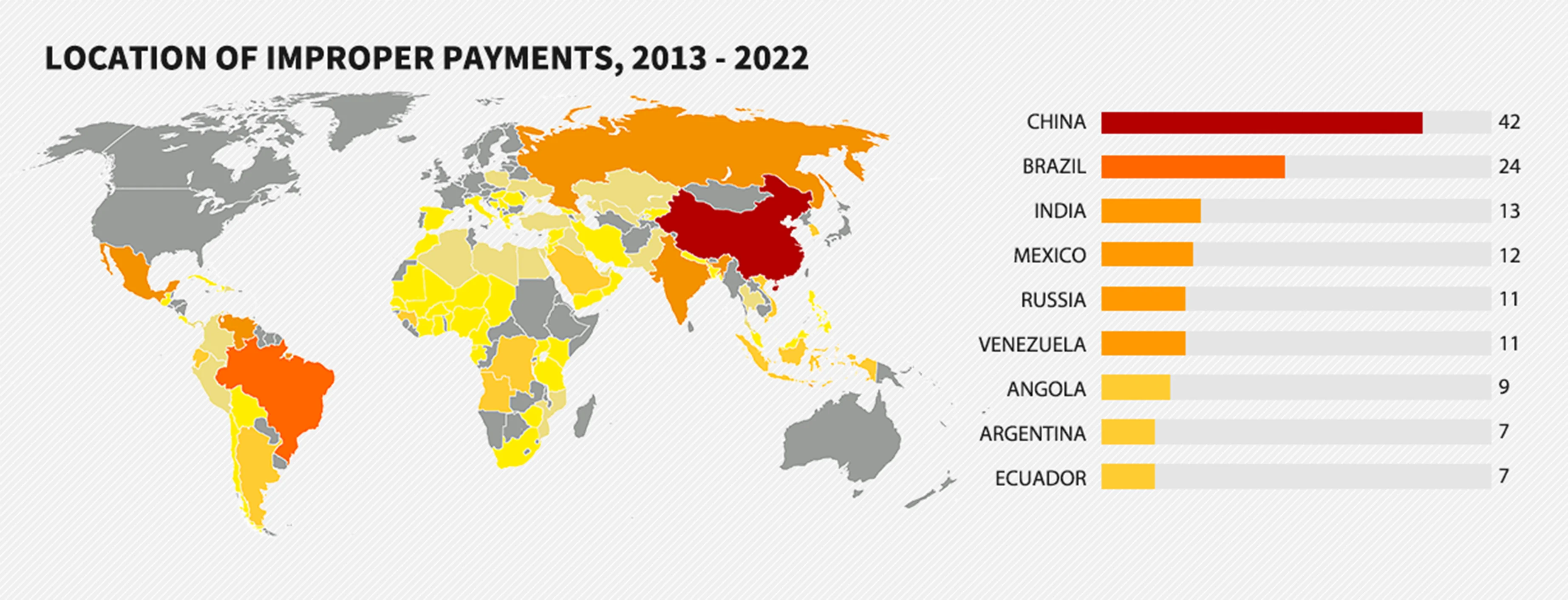
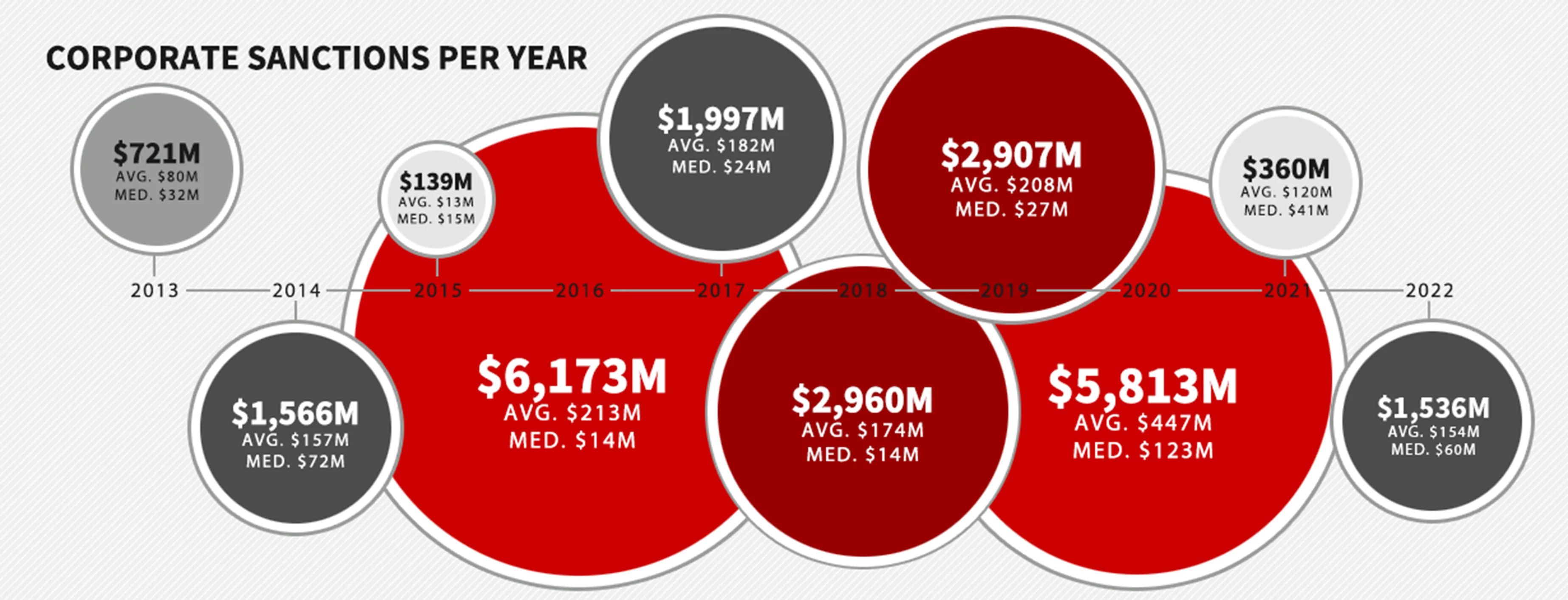
Countries across the globe are continuously working towards making their business ecosystem safe by passing regulations to prohibit bribery, corruption, money laundering and prevent fraud. Companies operating within national boundaries are regulated only by national laws, however businesses with cross-border teams, subsidiaries and subcontractors are also regulated by international laws. Read more about country-wise due diligence regulations here. Here is how a heatmap looks like the location of improper payments, 2013-2022.
Laws to Adhere for Companies Operating Within India
- The Companies Act, 2013 – All companies registered in India must comply with regulations stated by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to prevent money laundering.
- Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA)– All companies with foreign direct investment (FDI) are required to comply with FEMA.
Laws to Adhere for Companies Operating in International Markets
- The UK Bribery Act – The Bribery Act covers transactions that take place in the UK or abroad, and both in the public and private sectors.
- The US Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (FCPA) -The FCPA prohibits the payment of bribes to foreign officials to obtain and retain business. It applies to two broad categories of persons: those with formal ties to the United States and those who take action in furtherance of a violation while in the United States. U.S. “issuers” and “domestic concerns” must obey the FCPA, even when acting outside the country.
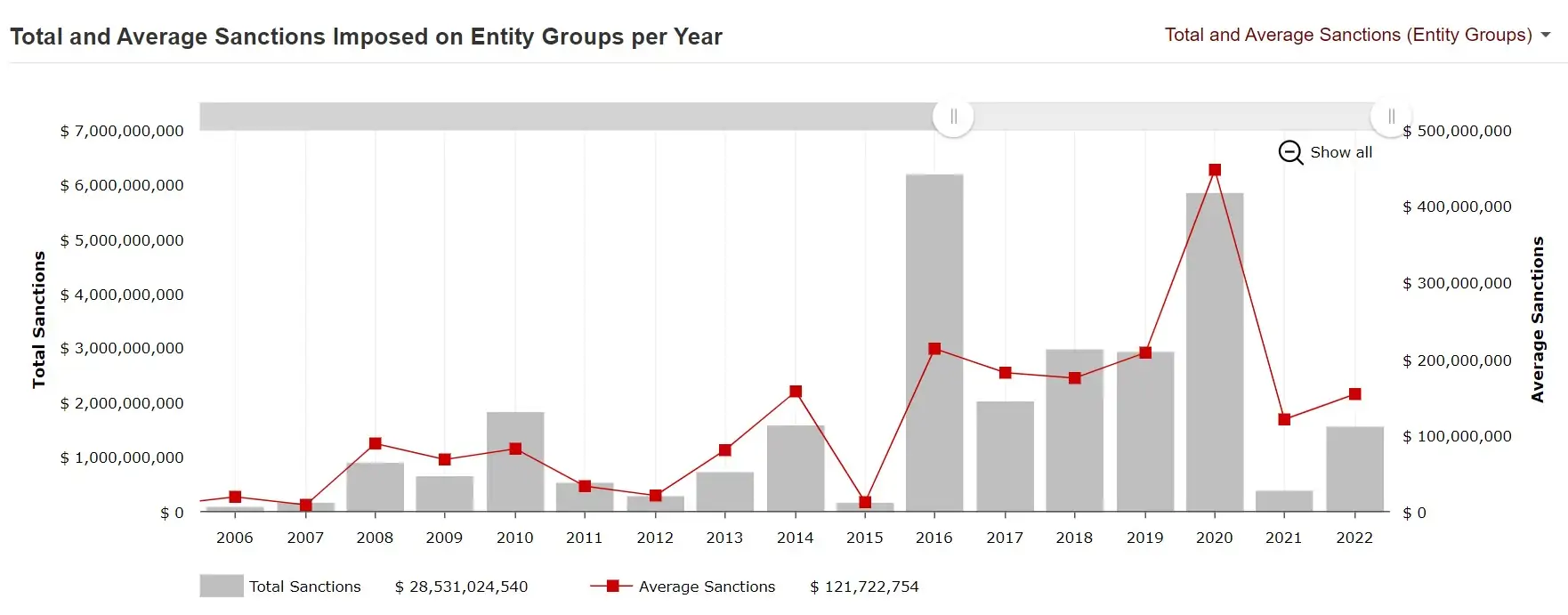
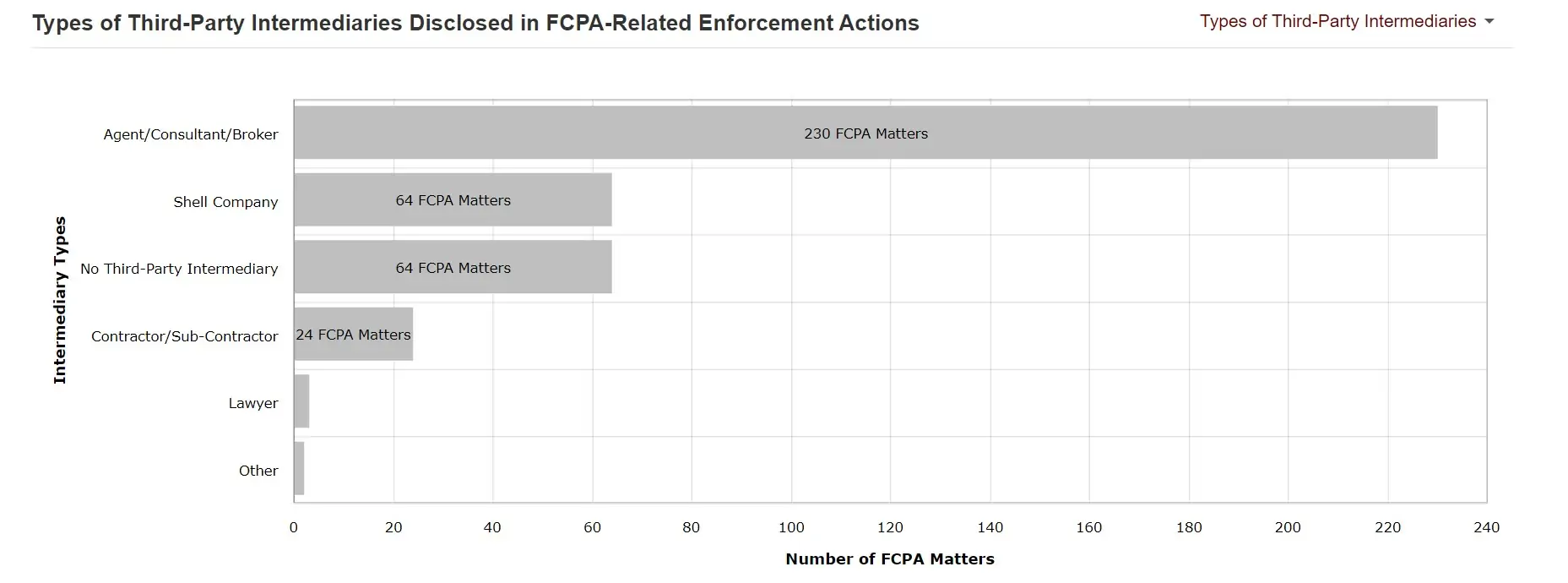
Key Stats from The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act Clearinghouse (FCPAC)
Total and Average Sanctions Imposed on Entity Groups
Types of Third-Party Intermediaries Disclosed in FCPA-related Enforcement Actions
Corporate Sanctions Timeline (2013-2022)
Understanding Your Due Diligence Requirements
Understanding your due diligence requirements could be a challenging task. But, with a team of experts and commitment, you can plan a thorough audit of your internal/external processes, stakeholders and business partners and how much of a risk they are exposed to.
What is a due diligence audit?
In a general sense, a due diligence audit examines a company’s standings, financial performance and exposure to different kinds of risks. The objective of the audit may vary based on one or more following business transactions.
Business Transactions that require Due Diligence
A well-thought due diligence framework enables informed decision-making in various business transactions. Broadly, there are five categories of business transactions that require thorough due diligence. These are
- Mergers and Acquisitions
- Investment Risk Due Diligence
- New & Existing Business Partnerships
- Joint Venture and Collaborations
- Public Offer
Requirements for due diligence often help you identify the right type of due diligence solution for your business. A few questions you need to consider to find the right fit are:
- Who are the stakeholders involved in the existing process?
- Type of process- internal, external?
- What level of competence is required from the stakeholders to conduct due diligence?
- Collection process, formats and storage of existing data of the parties in the purview of this exercise.
- Budget, the scope of process automation and target turnaround time.
Upon answering the above questions, the next step is to step up a due diligence process to Identify, screen, and minimise your risk exposure.
Risk Score-Based Due Diligence Process
The due diligence process typically involves several stages that may vary depending on your objective, industry, and your risk appetite. In a holistic sense, a typical due diligence process involves three major steps:
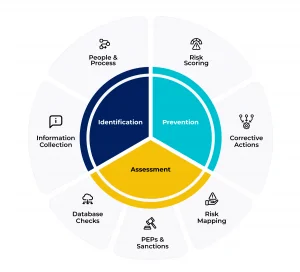
Identification
The first step involves identifying the gaps and factoring their risk exposure
- People & Process: involves working closely with the business owners and identifying the gaps in existing processes to map the level of risk involved
- Information Collection: involves what information needs to be collected. and from where will the information come?
- For businesses, the information required includes MCA registration, proof of address, compliance reports, shareholders, beneficiaries, stakeholding structure, and their political affiliations
- For individuals, the information required includes proof of identity, proof of address, financials, and political affiliations
Assessment
The second step is to assess the level of risk exposure based on the information collected
- Database Checks: This step involves cross-verifying the information collected and validating it against various national and international databases.
- PEPs & Sanctions: Screening against politically exposed persons and sanction lists become business to minimize reputational risk exposure.
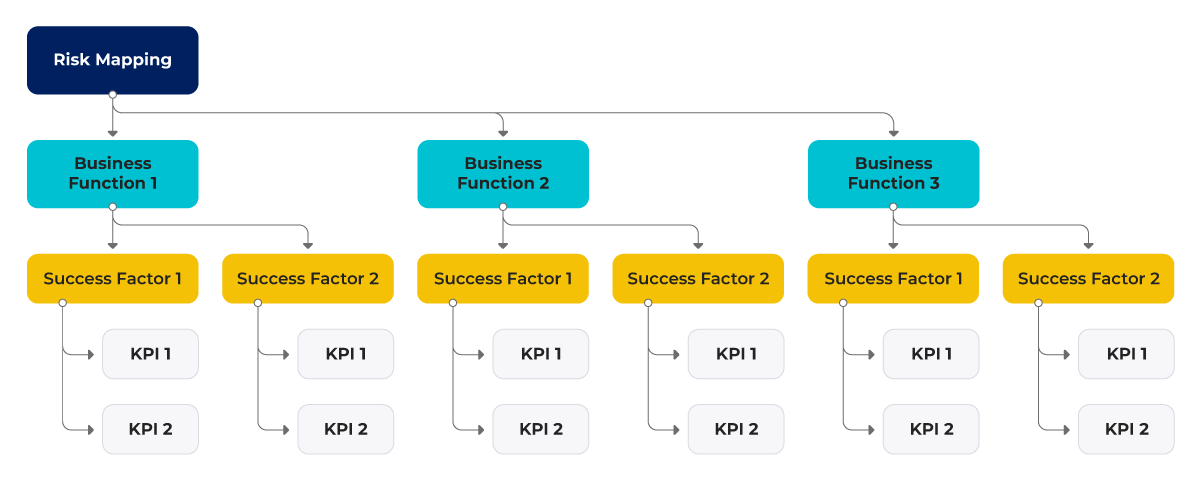
- Risk Mapping: This is a process of identifying the key areas prone to risk. The success factor for all the identified departments with KPIs to measure is defined
Prevention
The third step involves implementing mechanisms to mitigate risk assessed in step two
- Risk Scoring: Based on the benchmarks identified in step one a risk score is assigned to the business or an individual. Very often businesses categorize their risk score in a color-coded fashion i.e. Red, Amber, and Green.
- Corrective Actions: Based on the sensitivity of the case levels of risk are defined corrective courses of action are defined in the form of levels of due diligence i.e. Simplified, Standard, and Enhanced Due Diligence. More on this is below.
Three Levels of Due Diligence

Keeping risk-based due diligence in consideration, you can segment your customers into three risk categories i.e low, medium, and high in order to select the right level of due diligence for them. A clear delineation of the due diligence level will help you offer a pleasant onboarding experience with no unnecessary blockades.
Simplified Due Diligence for low-risk profiles
Simplified due diligence is the easiest risk assessment framework, ideal for a low-risk profile with negligible risk exposure. They generally include well-known public enterprises and individuals with impeccable financial records contributing to the lower ticket size of the overall revenue stream. While taking the route, you may only need to know the identity of the entity or the individual. However, storing the proof of qualification for simplified due diligence can ensure compliance and visibility if any corrective action is required in the future.
Standard Due Diligence for medium-risk profiles
Standard due diligence is the most commonly used risk assessment framework, the right fit for a medium-risk profile. This involves not just only knowing the identity but also verifying it to ensure they are who they claim to be. Verifying basic information like full name, date of birth, and address against a government-issued ID and other databases will help you filter potential threats preemptively.
Enhanced Due Diligence for high-risk profiles
Enhanced due diligence is the most detailed risk assessment framework, best suited for high-risk profiles. The high-risk profiles comprise your employees, customers, and business partners who need comprehensive screening and monitoring to keep a tight eye on identity thefts and credibility throughout the lifecycle and minimize risk exposure.
Below mentioned are some measures worth considering for both businesses and individuals
- Enhanced screening and identity verification
- Intended nature of the business partnership
- Financial of Entity & Individuals
- Third-party risk and compliance measures
- Process assessments and mystery audits
- Adverse media, Sanctions & Watch lists
- Ongoing Monitoring
Implementing Measures of Due Diligence
Depending on the budget and requirements you can choose between two types of due diligence services i.e. Offline and Online
- Offline Due Diligence – Organisations who are still going by the manual routes often require a due diligence report to onboard and verify individuals or entities.
- Online Due Diligence: Organisations either leverage a platform to onboard, verify & monitor their business partners or integrate verification APIs to collect due diligence reports directly into their ERPs.
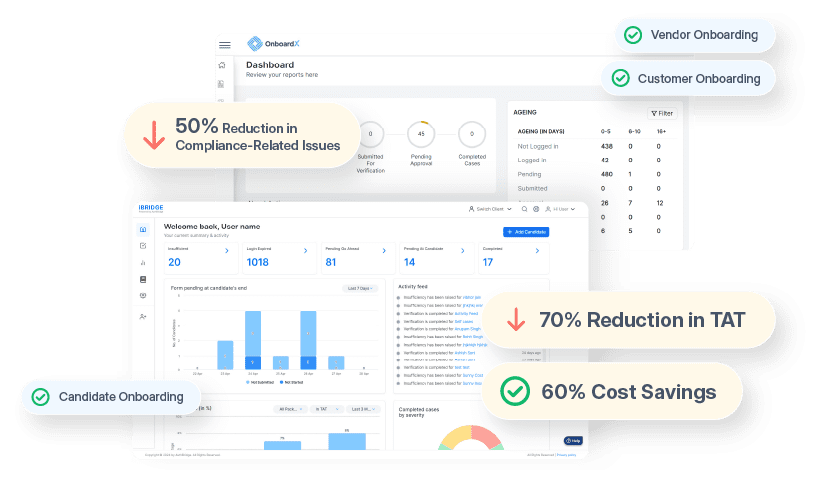
AuthBridge Due Diligence Solutions
With all the information at hand with the help of a due diligence solution you can now put the pieces of the whole puzzle together. A comprehensive due diligence solution will give access to all the requisite information and help you drive informed business decisions with data-driven insights. You may want to look at the offerings of the service providers and gauge them against your business needs.
From a bird’s eye view, your requirements may fall into three major categories. At AuthBridge business solutions, we call them
- Screening, Onboarding, and Verification: Know your Customer/Employee/Partner journeys at the time of first or repeated interactions with your business. You can choose from eKYC, DKYC, Video KYC or other types of KYC based on your needs.
- Risk Mitigation: Process assessments, Compliance Audits, and Business intelligence reports of your customers, partners, and third parties during all interactions with your business. You can choose from various Standard and Comprehensive due diligence reports.
- Fraud Prevention: Red flag fraudulent profiles for identity, customer, and financial fraud along with other suspicious transactions with the help of setting up an ongoing monitoring process at defined intervals.
AuthBridge has 17+ years of experience in providing digital solutions for background verification and due diligence to small, medium, and large enterprises across 20+ industries.
Have any questions about due diligence? Reach out to a team of experts to understand your due diligence needs.